Foundation and its function & Classified

Foundation and its function & Classified
The same way humans have their feet to transfer their self weight and other loads, softly to the ground, foundations carry with light pressures the structural frame loads to the underlying soil. Foundation generally includes the footings and the pedestals. The simplest type of foundation is the spread foundation (pad foundation) i.e. isolated column footings.
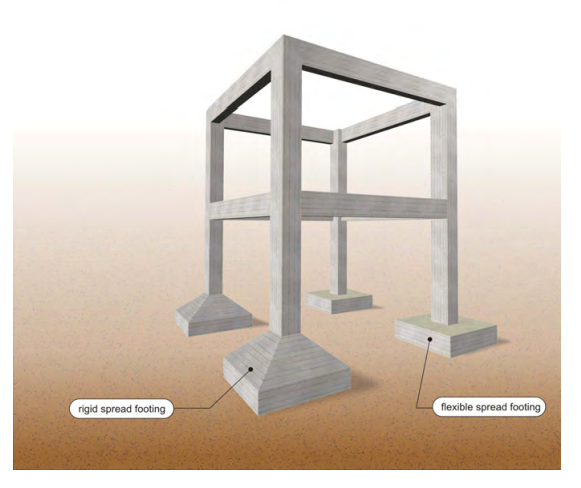
Foundation consisting of flexible and rigid spread footings (no connecting beams)

As a rule, spread footings consist only of a box and they are usually called flexible. Sometimes they may have a relatively large height and a sloped end, and they are called rigid.Nowadays, flexible spread footings are used almost exclusively because of their easy construction and their low cost and labor. However in the past, when the material cost was higher than the labor cost, rigid spread footings were usually constructed.
The footings’ dimensions depend on the soil’s quality and the loads transferred by the columns (column loads are determined by the distance between the columns along with the number and loads of the structure’s storeys). The usual footing dimensions range from 1.0×1.0m to 3.0×3.0m although sometimes they may be larger and their height varies between 0.50m and 1.00m for flexible spread footings and between 0.70 and 2 m for rigid spread footings.
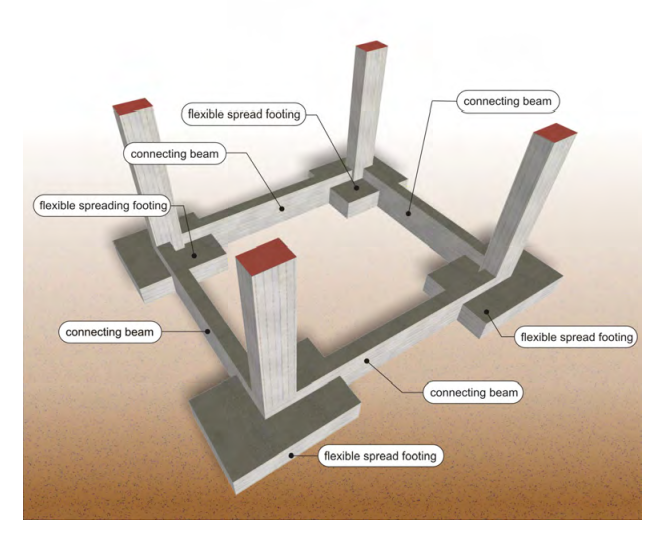
Foundation consisting of flexible spread footings and connecting beams

In order to ensure the proper behavior of the foundation, the use of foundation beams (connecting beams) is mandatory. These beams tie together the column’s bases thus making the footings behave in a normal way especially during seismic incidents. Usually their cross section width ranges from 0.30m 0.50m and their cross section height from 0.50m 1.50m.
Footings are constructed centrically to their mass centre, except in those cases when due to building restrictions they are eccentrically constructed e.g. like boundaries of the building line or edge of the building land as shown below.
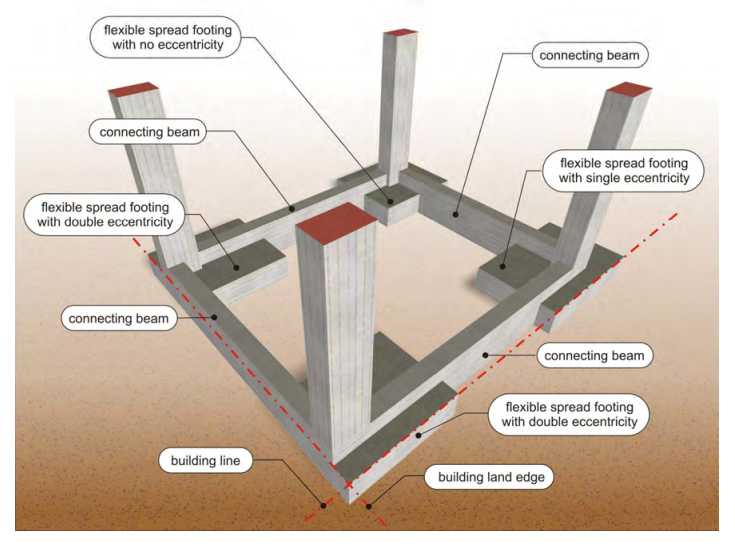
Foundation consisting of eccentrically constructed spread footings due to limitations of the building line and the edges of the building land The bigger the footing’s construction eccentricity is, the strongest must the connecting beam in that direction be.
Spread foundation (pad foundation) is used in a good quality soil. In case of low soil capacity strip foundation is used.

Strip foundation with connecting beams
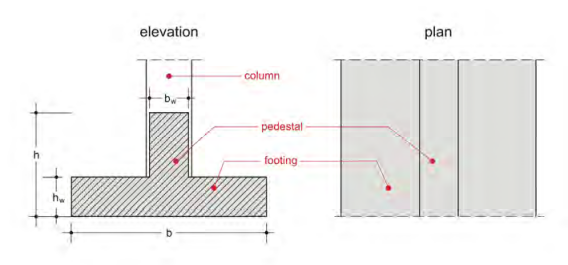
Strip foundation consists of the pedestal and the footing. The usual dimensions of the footing vary between 0.40m to 0.60m for its thickness and between 1.00m to 2.50m for its width. The typical pedestal cross sections range from 0.30×0.80 to 0.50×1.50.
For a more effective behavior it is advisable to use grid foundation.In poor soil conditions raft foundation is commonly constructed. It consists of a slab which extends over the entire loaded area. Frequently it is used in other soil conditions for practical reasons basically because of its fast and easy construction.
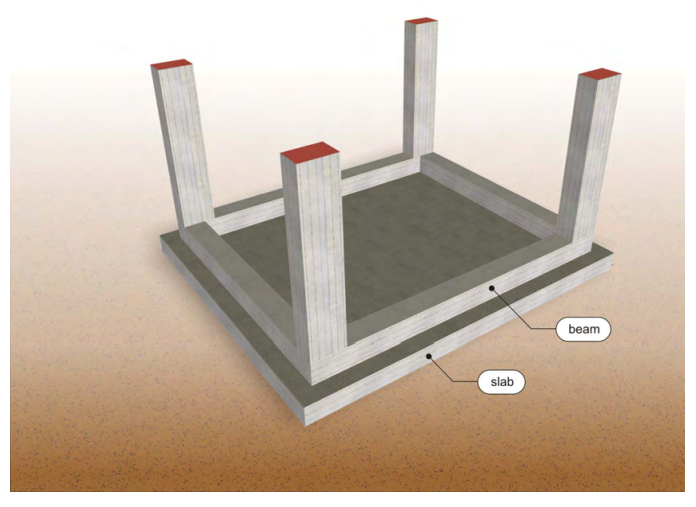
Raft Foundation with connecting beams
Raft foundation may have regular foundation beams for rib formation, as shown in the above figure, or beams incorporated into the foundation with the form of hidden beams.The usual thickness of a raft foundation, ranges from 0.40m to 1.0m, while the dimension of the raft foundation beams vary from 0.30×0.80 to 0.50×2.00.

Two level foundation
Generally foundation should be placed in one even level however in certain cases like sloped building lands, foundation is placed on more than one levels.








